Risk Assessment and Treatment Process
Introduction
This is the Risk Management process that goes together with Risiko365.
Responsibilities
The Information Security Manager (ISM) is responsible for carrying out risk assessments wherever they are required by the ISMS or when significant changes are proposed or occur.
You can also use the Recurring Management System Action (RMSA) module in Risiko365 to setup reminders for a regular review of the risk register.
Within each risk on the risk register you can also set a review date that will remind you to review that specific risk.
Information Asset
Determine the asset category and the asset:
- People (including staff, customers, subscribers, suppliers and any other person within scope that is involved with storing or processing of information)
- Hardware, Infrastructure / Utilities & Physical items (including computer and communications equipment, media (paper, tapes, CDs and disks), and other technical equipment (power supplies, air-conditioning units), and buildings that are used to support the processing of information)
- Software and firmware (including application software, system software, development tools and utilities, databases)
- Information (Including customer information, supplier information, proprietary information, organizational information)
- Paper Documentation
- Processes & Services (including business processes, application specific activities, computing and communications services and other technical services supporting the processing of information (heating, lighting, power, air-conditioning services)
- Third party suppliers
- Company Image & Reputation
Risiko365 will provide a list of typical asset categories and assets. These lists can easily be amended by clicking the “+” sign and adding your own assets.
Number of assets
Determine number of assets. If you have a number of assets that are of the same type, these can be assessed as a group (i.e. laptops with same software).
Process based risk assessment
Risks can also be identified without being specifically related to an asset or asset category, i.e. you leave the asset fields empty.
Risk Assessment
Identify the risks
The risks to your information assets are identified. Risiko365 will provide a dropdown list with options or you can add your own options by clicking the “+” sign.
For each risk select the appropriate impact on availability, confidentiality and integrity (CIA). Simply tick the relevant CIA boxes.
Impact
The impact that losses of availability, confidentiality and integrity might have are determined and documented. Risiko365 will provide dropdown list with options or you can add your own options by clicking the “+” sign.
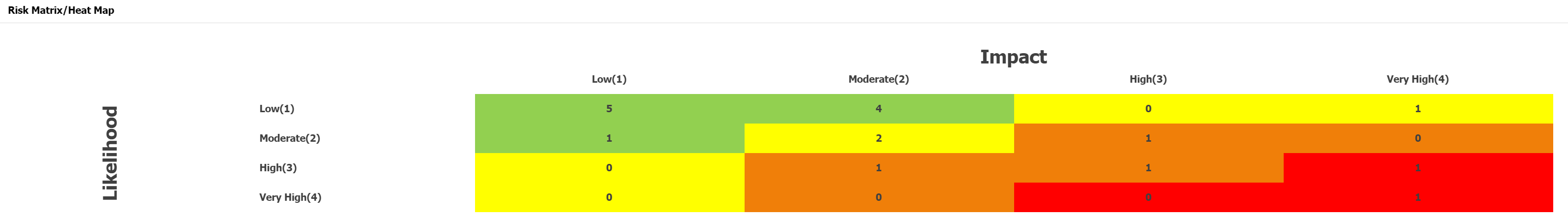
Score the likelihood and impact
The risk levels are determined using the formula: LIKELIHOOD + IMPACT = RISK using 3+3 matrix provided below.
OR
The risk levels are determined using the formula: LIKELIHOOD x IMPACT = RISK using 4×4 matrix provided below.
Risk Priority
3+3 Matrix
4×4 Matrix
NOTE: Above is showing two examples of risk scoring methodologies (3+3 (0-2) and 4×4). Risiko365 offers more risk scoring methodologies (3+3 (1-3), 3×3, 5×5, 6×6 and 7×7), and the tables above would need to be amended depending on the chosen methodology.
All risks are reviewed by the Information Security Committee (ISC) and are prioritised based on the risk score.
Treatment options are:
- Selection of controls
- Transfer of risks to a third party
- Risk avoidance
- Risk acceptance
Risk Treatment Plan
Mitigating action
For each of the risks, identify the possible options for treating and document which mitigating action is going to be taken.
Select controls for treatment of the risks
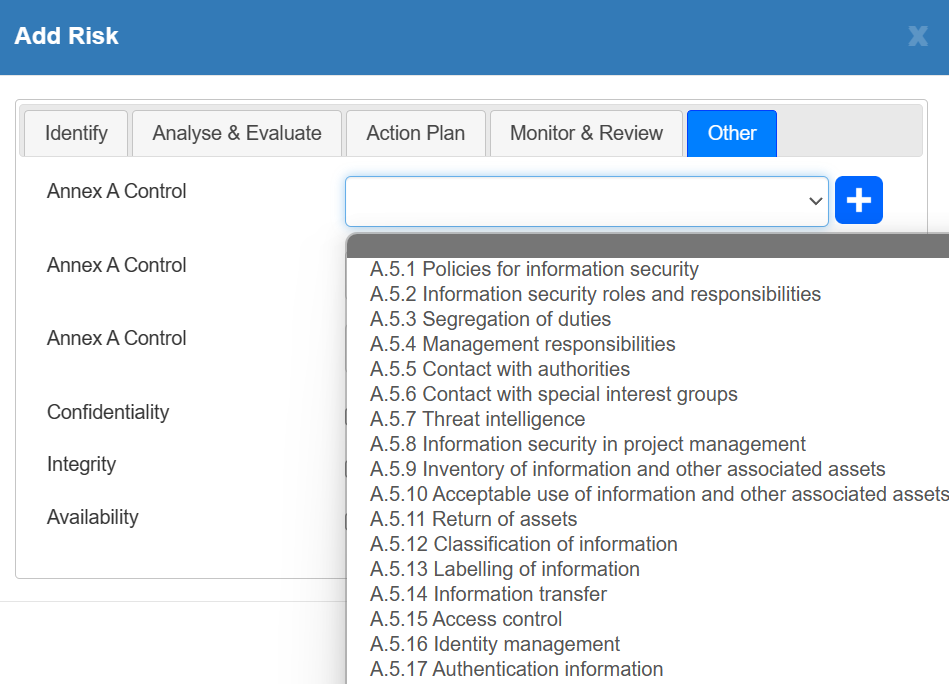
Appropriate control objectives are selected or designed according to the specific needs of the risk and the organisation and controls to achieve those objectives are selected from a variety of sources.
Controls selected are compared against those from Annex A of ISO27001:2022 to ensure that none have been missed.
Treatment Planning
For each risk, identify the risk owner. The risk owner should be a manager within your organisation.
The risk owner will plan the risk mitigation by establishing resources required and a due date for the implementation of the controls.
Residual risk
Following the mitigating action for the risk perform a new risk assessment and rescore likelihood and impact, and a new risk score is calculated (known as the residual risk score).
Risiko365 will keep the initial risk score until you select that risk treatment has been implemented (selecting “Yes” as Treatment Implemented).
If the residual risk is accepted by management this is recorded. If the residual risk score is not accepted further mitigation would be required.
Definitions
Asset
An asset is broadly defined as ‘anything, which has value to an organisation, its business operations and its continuity’. If the confidentiality, integrity or availability of an asset is compromised then there will be an impact felt by the business or other stakeholders.
CIA
CIA refers to Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability. Confidentiality of information, integrity of information and availability of information. Many security measures are designed to protect one or more facets of the CIA triad.
Confidentiality
Confidentiality is concerned with protecting the information asset from access or disclosure to unauthorized parties.
Integrity
Integrity means maintaining and assuring the accuracy and consistency of information assets over their entire life-cycle. This means that data cannot be modified in an unauthorized or undetected manner.
Availability
Availability refers to ensuring that authorized parties are able to access the information asset when needed.
Risk
In general terms an information risk can be thought of as the likelihood that a threat will exploit a vulnerability leading to a business impact.
Threat
The potential danger that a vulnerability may be exploited intentionally, triggered accidentally, or otherwise exercised.
Threat Agent
A means or method used to exploit a vulnerability in a system, operation or facility.
Vulnerability
A potential or actual flaw or weakness in system security procedures, design, implementation, or internal controls that could be exercised (accidentally triggered or intentionally exploited) and result in a compromise of the integrity, availability, or confidentiality of an information asset.
Impact
Adverse change to the level of business objectives achieved.
Likelihood
Is the probability that a threat caused by a threat-source will occur against a vulnerability.
Risk Treatment
Risk Treatment is the process of selecting and implementing of measures to modify risk.
Treat
Actions taken to lessen the probability, negative consequences, or both, associated with a risk. This enables you to continue with the activity/objective but with controls and actions in place to maintain the risk at an acceptable level.
Transfer
Transferring the risk with a third party to lessen the burden of loss such as the use of an insurance policy.
Tolerate
Acceptance of the burden of loss or benefit of gain from a particular risk, usually taken if you have a limited ability to mitigate the risk or the cost of mitigation may be disproportionate to the benefit gained.
Terminate
Some risks can only be contained at an acceptable level by terminating the activity, alternatively senior management or the executive can dismiss (terminate) the risk.
Intangible Asset
An asset that is not physical in nature. Corporate intellectual property (items such as patents, trademarks, copyrights, business methodologies), goodwill and brand recognition are all common intangible assets in today’s marketplace. An intangible asset can be classified as either indefinite or definite depending on the specific Adapt of that asset. A company brand name is considered to be an indefinite asset, as it stays with the company as long as the company continues operations. However, if a company enters a legal agreement to operate under another company’s patent, with no plans of extending the agreement, it would have a limited life and would be classified as a definite asset.